- test-pod.yaml
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: test-pod #Pod이름 labels: env: prod spec: containers: # - 기준으로 복수개 단위묶음 - image: repo/hellotest #생성할 컨테이너 이미지 name: hellotest ports: - containerPort: 8080 #생성될 애플리케이션의 응답포트 - kubectl create -f test-pod.yaml // Pod 생성.
- kubectl get pod test-pod -o yaml // Pod의 yaml 확인.
- kubectl describe pod test-pod // Pod의 발생한 이벤트 확인.
- kubectl logs test-pod 혹은 kubectl logs test-pod hellotest // Pod의 콘솔로그.
- kubectl port-forward test-pod 8888:8080 // 컨테이너 8888 을 -> Pod 8080 로 포트포워딩 'bg 프로세스' 뜸!
- curl 127.0.0.1:8888 // 해당 Pod으로 접속 가능.
- kubectl label pod test-pod rel=alpa
- kubectl get pod --show-labels 혹은 kubectl get pod -L rel // 특정 라벨 보기
- kubectl get pod -l 'env=prod,rel!=beta' // 특정 라벨 값 셀렉터
- kubectl delete pod test-pod
-
- test-replicaset.yaml
-
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: ReplicaSet metadata: name: test-replicaset spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabel: # matchExpressions 으로 더 강력한 셀렉터 가능. app: hello # 관리할 Pod의 라벨. template: # Pod.yaml의 내용을 작성. metadata: labels: app: hello spec: containers: 동일하게 작성 - kubectl apply -f test-replicaset.yaml
- kubectl get rs
- kubectl scale rs test-replicaset --replicas=10
- kubectl describe rs test-replicaset
-
- test-deployment.yaml
-
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: test-deployment spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabel: app: hello template: 동일하게 작성 - (ReplicaSet의 상위 리소스로, 다운타임 없이 롤링업데이트)
- kubectl apply -f test-deployment.yaml
- kubectl get deploy
- kubectl edit deploy test-deployment # 직접 수정을하여, 복제수 스케일링
- kubectl scale deploy test-deployment --replicas=10 # 커맨드로 복제수 스케일링
-
- namespace
- 다양한 환경의 각 리소스들를 `네임스페이스`로 나누어서 관리.
- application-system, default, kube-public, kube-system 등등
- 즉, 특정 `네임스페이스`에서 각각의 리소스에 이름이 고유해 지는것!
- kubectl create ns test-namespace # 굳이 yaml 작성해서 만들수도 있음...
- kubectl get ns
- kubectl get pod -n test-namespace
- 다양한 환경의 각 리소스들를 `네임스페이스`로 나누어서 관리.
- Services
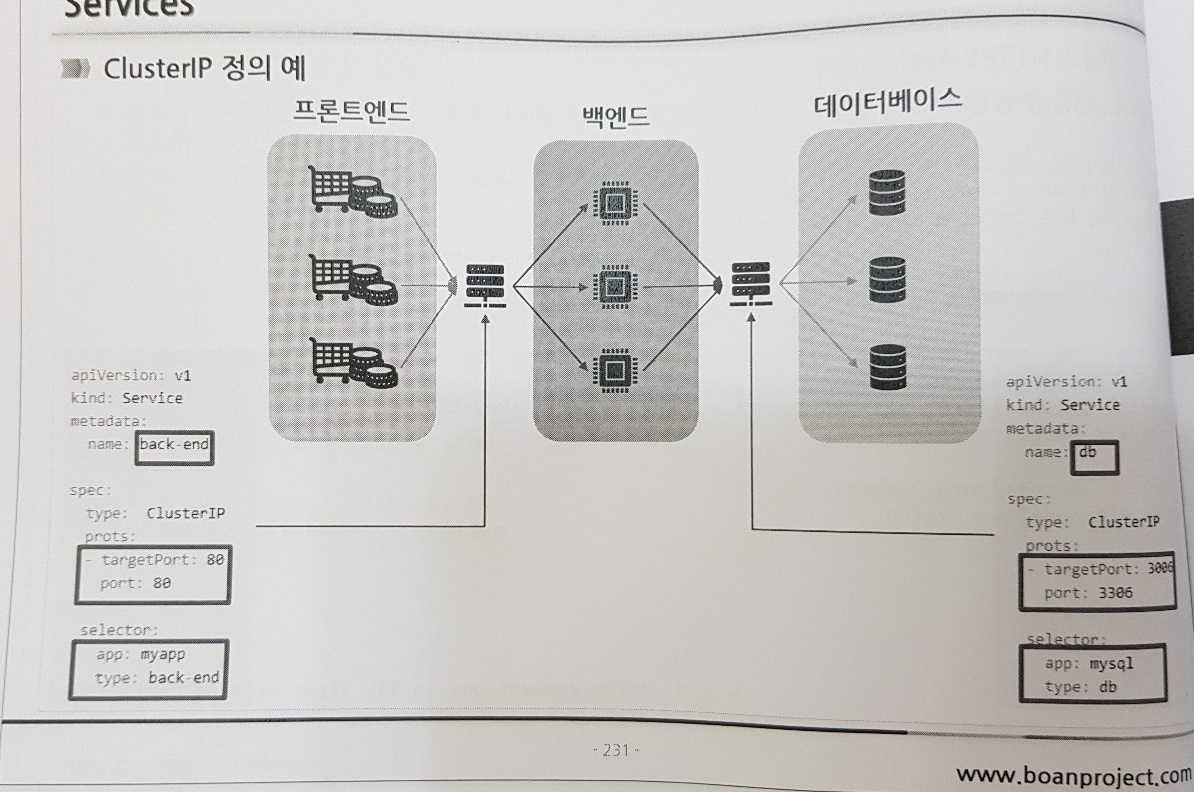
- Pod는 가변적인 컨테이너의 집합이기 때문에, 서비스에 한계가 있음.
- 즉, 별도의 IP로 Pod를 묶고~ 로드밸런싱을 관리하는 리소스가 필요함.
- test-service.yaml
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: test-service spec: sessionAffinity : ClientIP # 다수 POD 구성시, client ip 기준으로 세션유지. ports: - name: http port: 80 targetPort: 8880 - name: https port: 443 target: 8443 selector: app: hello - kubectl create -f test-service.yaml
- kubectl get svc # ClusterIP 생성 확인. (외부IP 없음)
- kubectl describe svc test-service
- kubectl exec -it {이름} /bin/bash -> curl {아이피}:{포토} -> 내부접속확인
- 다수의 POD를 ClusterIP 서비스로 묶어서 POD간 통신하는 아키텍쳐
- 서비스를 노출하는 3가지 방법
- 1) NodePort
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: test-nodeport spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 80 # 서비스의 포트 targetPort: 8080 # POD의 포트 nodePort: 30001 # 최종적으로 서비스되는 포트 selector: app: hello - 노드를 사용하여(?) 포트 리다이렉션.
- 워커노드를 말하는 건가?
- [외부 -> ? -> 노드:30001 -> Service:80 -> POD:8080]
- kubectl create -f test-nodeport.yaml
- kubectl get svc # NodePort 생성 확인.
- kubectl get node -o wide # Node 생성 확인. (외부IP 있음)
- curl {nd외부IP}:30001
-
- 2) LoadBalancer
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: test-loadbalancer spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 # 최종적으로 서비스할 포트 targetPort: 8080 # POD의 포트 selector: app: hello - 로드밸런서의 고유한 IP를 가지고, 그를 통해서~ 서비스로 포트 리다이렉션.
- [외부 -> LB서비스:80 -> ?노드:30xxx? -> POD:8080]
- (내부적으로 NodePort 기능을 기반으로 동작)
- kubectl create -f test-loadbalancer.yaml
- kubectl get svc # LoadBalancer 생성 확인. (외부IP 있음)
- curl {lb외부IP}:80
-
- 3) Ingress
-
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: test-ingress spec: rules: - host: www.test.com # 도메인이 일치하지 않으면 안됨. http: paths: - path: / backend: service-name: test-service # 연결할 서비스 servicePort: 80 - host: api.test.com http: paths: - path: / backend: service-name: test-api-service servicePort: 8080 - (각 서비스를 LB기반, 각각에 별도의 IP로 하지않고~)
- 인그레스 하나의 IP를 가지고, 여러게의 서비스로 포트 리다이렉션.
- [외부 -> 인그레스 -> `서비스명` -> 서비스 -> 노드 -> POD]
- kubectl create -f test-ingress.yaml
- kubectl get ingresses # Ingress 생성 확인. (Address 있어야 정상)
- vi /etc/host # 해당 도메인을 -> Address으로 호스팅 해야함.
- curl http://{도메인}
- 인그레스를 활용한, 로드밸런싱 프로세스 확인
- https://www.notion.so/GKE-1ad380a39042434ba71ae286c1560af8
-
-
- Kubernates 내부 Network 모델
- 모든 POD는 자체 IP 주소가 있고, 모든 POD간 통신이 가능하다.
- CoreDNS :
- 내부적으로 DNS 역할을 하는 POD.
- 서비스를 생성되면, "{서비스명}.{네임스페이스}.svc.cluster.local" 로 관리되고~ 내부통신 되는것!
- POD에서도 (서비스명과 일치한) 서브도메인을 설정하면, DNS 관리가 가능하다.
- Storage
- 다수의 컨테이너가 접근 및 공유 할수있는, 퍼시스턴트한 데이터저장이 필요함.
- (별도의 k8s 리소스는 아니고) POD 스펙으로 '스토리지 볼륨'을 제공함.
- 스토리지 종류
- 1) 임시볼륨(emptyDir)
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: test-tempvolume spec: containers: - image: repo/hellotest name: hellotest volumeMounts: # 각 Pod에 마운트 - name: hellovol mountPath: /var/... - image: repo/hellotes2 name: hellotes2 volumeMounts: # 각 Pod에 마운트 - name: hellovol mountPath: /usr/... readOnly: true ports: - containerPort: 80 volumes: # 볼륨설정 - name: hellovol emptyDir: {} - 간편하게 POD에 '빈공간의 디렉토리'를 정의하고, 각각의 컨테이너에 마운트하여 공유 가능.
- 해당 POD가 해제되면, 당영히 함께 사라지는... 영구적이지 않음.
-
- 2) 로컬볼륨(HostPath,Local)
- 호스트 로컬의 파일시스템에 있는 특정 파일 or 디렉토리를 지정 할 수 있음.
- 당연히, 해당 POD가 해제되어도 사라지 않음.
- 곰곰히 생각해보면, 해당 로컬의 POD 와 아닌 POD간에는 공유가 안되는 ㅎㅎ;
- kubectl get pod {이름} -o yaml -n kube-system # POD가 마운트한 HostPath 볼륨 확인가능.
- 3) 네트워크볼륨(nfs 등등)
- NAS같은, 기존의 NFS를 POD에 장착 할 수 있음.
- 4) 상용클라우드 네트워크볼륨
- GcePersistanceDisk :
- 구글 클라우드에서 제공하는 디스크 마운트.
- ...
- AwsElasticBlockStore :
- ...
- PersistentVolumeClaime :
- 추상화를 통해서, 특정 클라우드를 몰라도~ PersistentVolume 요구사항을 처리하는 리소스!
- POD -참조-> PVC -바인딩-> PV -마운트-> {특정 클라우드 디스크}
- persistent-volume.yaml
- ...
- persistent-volume-claim.yaml
- ...
- kubectl get pvc 및 kubectl get pv 으로 확인 가능.
- "동적 PV 프로비저닝" 으로 더 효율적인 자동화도 제공함.
- GcePersistanceDisk :
- 어어
-끝-
'DevOps' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CircleCI (0) | 2020.11.23 |
|---|---|
| K8S 애플리케이션 (0) | 2020.07.19 |
| Dockerfile (0) | 2020.07.09 |
| Docker-Swarm (0) | 2020.04.06 |
| Kubernetes 란? (0) | 2019.11.04 |